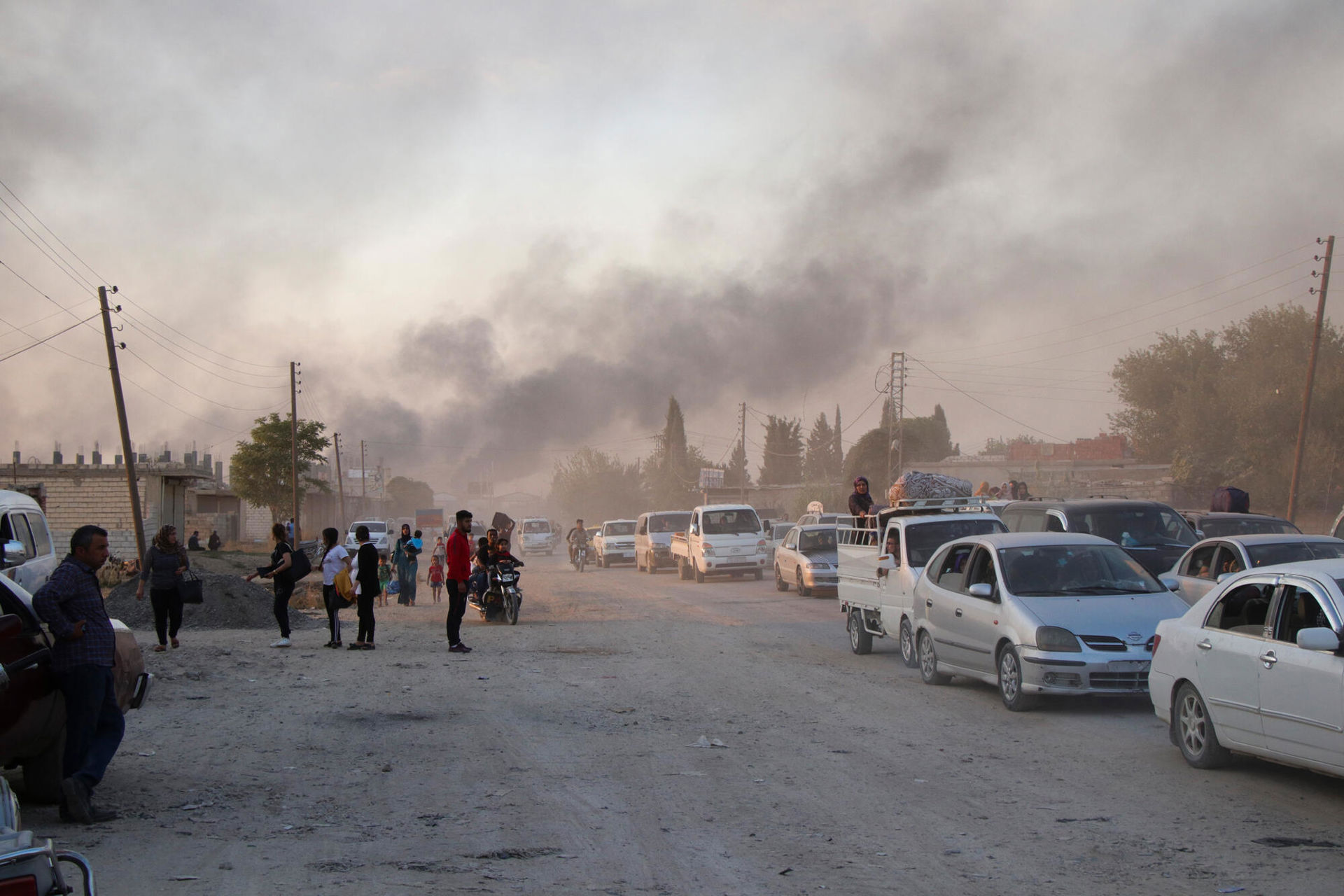
Since the start of the war in Syria 10 years ago, the lives of Syrian people have been under threat. Back in 2011, the situation quickly shifted from localised protests to a full-scale war, leading to a devastating humanitarian situation that persists a decade later. In the course of 10 years, 12 million Syrians – half the pre-conflict population – have been forced to flee the conflict and leave their homes behind, often multiple times, making it the biggest displacement crisis of this century. Many of them are still displaced today.
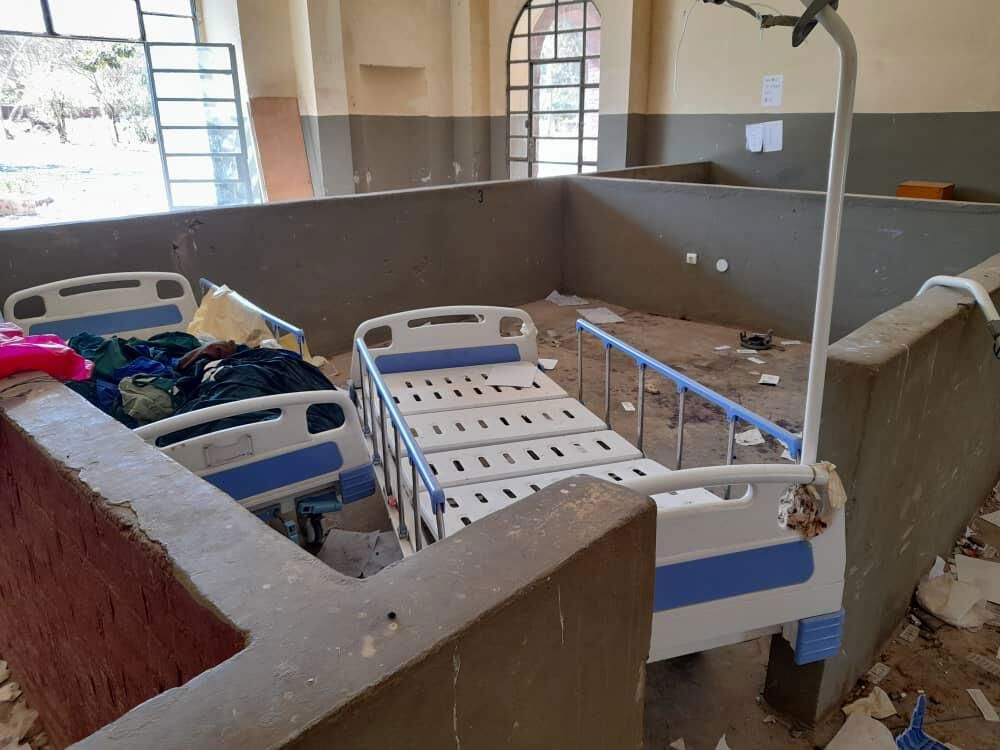
A significant part of Syria’s infrastructure has also been destroyed during the years of conflict. Notably, Syria’s relatively functional health system has been devastated. Hundreds of medical facilities have been bombed, large numbers of medical staff have been killed or have fled, and there are still desperate shortages of medical supplies in many parts of the country. Today, the medical needs of the Syrian population are huge.
Médecins Sans Frontières/Doctors Without Borders (MSF) has been responding to the crisis in Syria since its start. The international medical organisation has been providing support to people in need across different areas of the country: from donating medical supplies, to setting up hospitals and clinics, to providing remote support to medical facilities and networks of doctors in areas that MSF could not access directly. Today, MSF is providing support to Syrians within Syria as well as in various neighbouring countries that host Syrian refugees.
This timeline outlines a decade of conflict, highlighting the increasing humanitarian and medical needs of millions of Syrians and MSF’s efforts to respond to them.
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 |
2011: Protests turn to armed conflict
In 2011, large numbers of Syrians took to the streets to demand democratic reforms. The uprising quickly evolved from initially minor protests into massive protests during March. The protests were met with police and military violence, mass arrests and a brutal crackdown, resulting in hundreds of deaths and thousands of wounded. As the protests turned into conflict, Syrians started leaving their hometowns, either for different parts of the country or fleeing to neighbouring countries.
For MSF, providing medical care to people within Syria proved challenging from the start of the conflict. Indeed, from 2011 until today, MSF has not been granted approval to work in government-controlled areas of Syria, despite repeated requests for permission; as a result, our areas of intervention have always been concentrated on areas outside government control.
 War-wounded reach Jordan, June 2011.Initially opened in 2006 to treat war-wounded from Iraq, MSF’s reconstructive surgery hospital in Amman, Jordan, receives its first wounded patients from across the border in Syria.©Alessio Mamo
War-wounded reach Jordan, June 2011.Initially opened in 2006 to treat war-wounded from Iraq, MSF’s reconstructive surgery hospital in Amman, Jordan, receives its first wounded patients from across the border in Syria.©Alessio Mamo
MSF still managed to provide medical assistance to people in need within Syria by supporting networks of Syrian doctors and providing donations of medical and relief items to field hospitals and clinics in Homs, Idlib, Hama and Dara’ provinces. Unable to access the capital, MSF made donations to the Syrian Red Crescent in Damascus in response to the increasing medical needs and lack of medical supplies in the city.
In neighbouring countries such as Lebanon and Jordan, MSF started supporting Syrians who needed medical care that was unavailable inside Syria and set up projects to assist refugees who had started to flee the violence in their country.
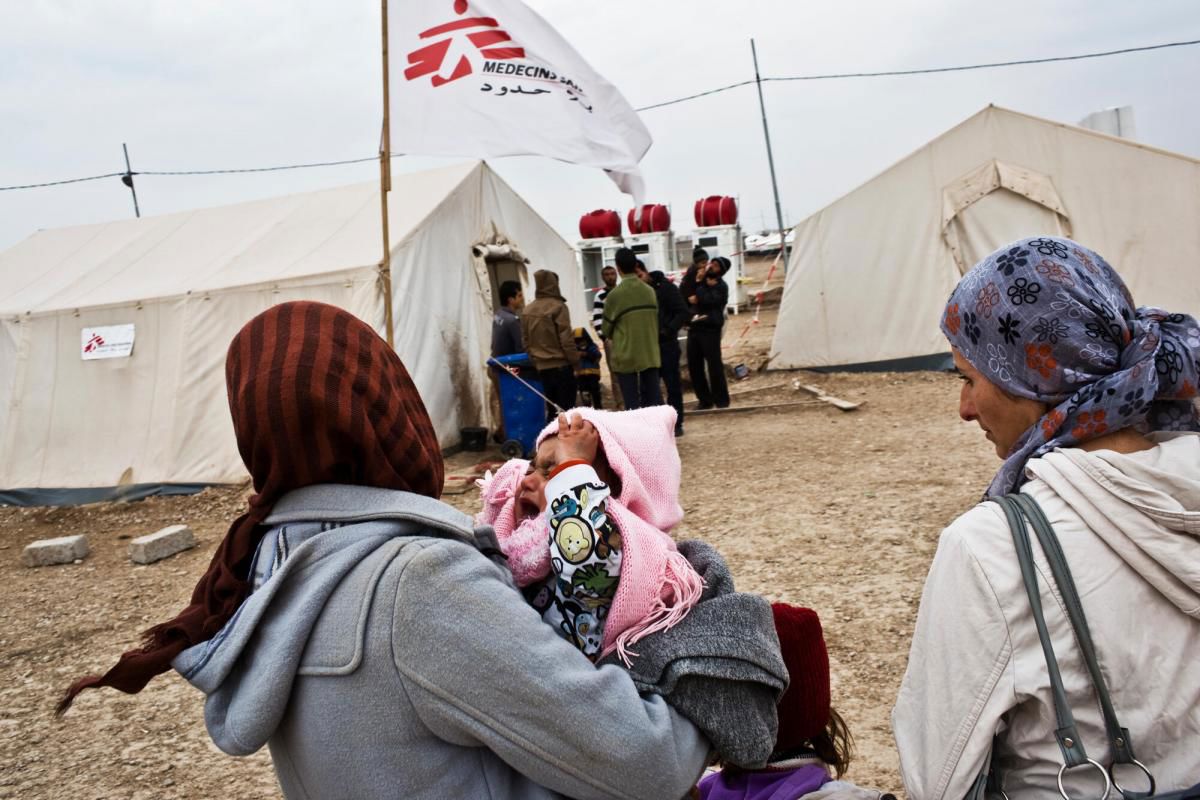
 Syrian refugees in Lebanon, 2011. MSF provides medical care to Syrian refugees in three locations in Lebanon: Tripoli, Wadi Khaled and the Bekaa Valley. ©Michael Goldfarb/MSF
Syrian refugees in Lebanon, 2011. MSF provides medical care to Syrian refugees in three locations in Lebanon: Tripoli, Wadi Khaled and the Bekaa Valley. ©Michael Goldfarb/MSF
2012: A full-fledged war
In 2012, the conflict escalated, with the formation and participation of different parties to the conflict. Despite various attempts to arrange a ceasefire, the conflict soon evolved into a full-fledged war and the number of deaths and injuries increased drastically across the country.
MSF opened hospitals across northern Syria to respond to people’s increasing medical needs in these areas. Most had to be set up in unconventional places, including villas, chicken farms, schools and basements, after a number of medical facilities were hit and destroyed in the conflict. In these hospitals, MSF teams provided emergency medical treatment with a major focus on trauma care and war-related surgeries.
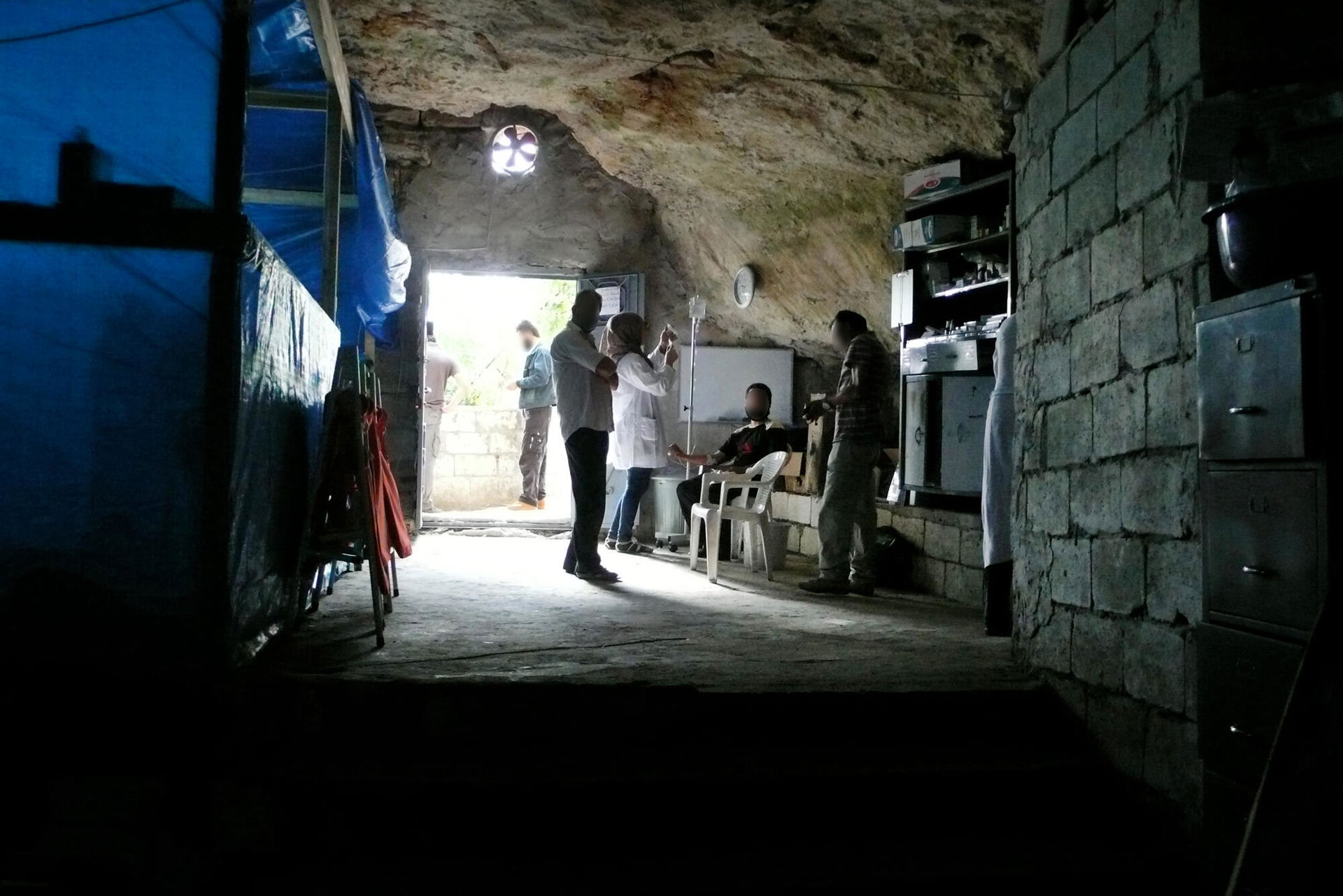 Cave transforms into hospital, August 2012.Close to Syria’s border with Turkey, MSF sets up a hospital inside a cave previously used for storing fruit, vegetables and fuel. Despite major logistical and medical challenges, the MSF team creates a sterile surgical unit suitable for providing emergency care and trauma surgery.©MSF
Cave transforms into hospital, August 2012.Close to Syria’s border with Turkey, MSF sets up a hospital inside a cave previously used for storing fruit, vegetables and fuel. Despite major logistical and medical challenges, the MSF team creates a sterile surgical unit suitable for providing emergency care and trauma surgery.©MSF
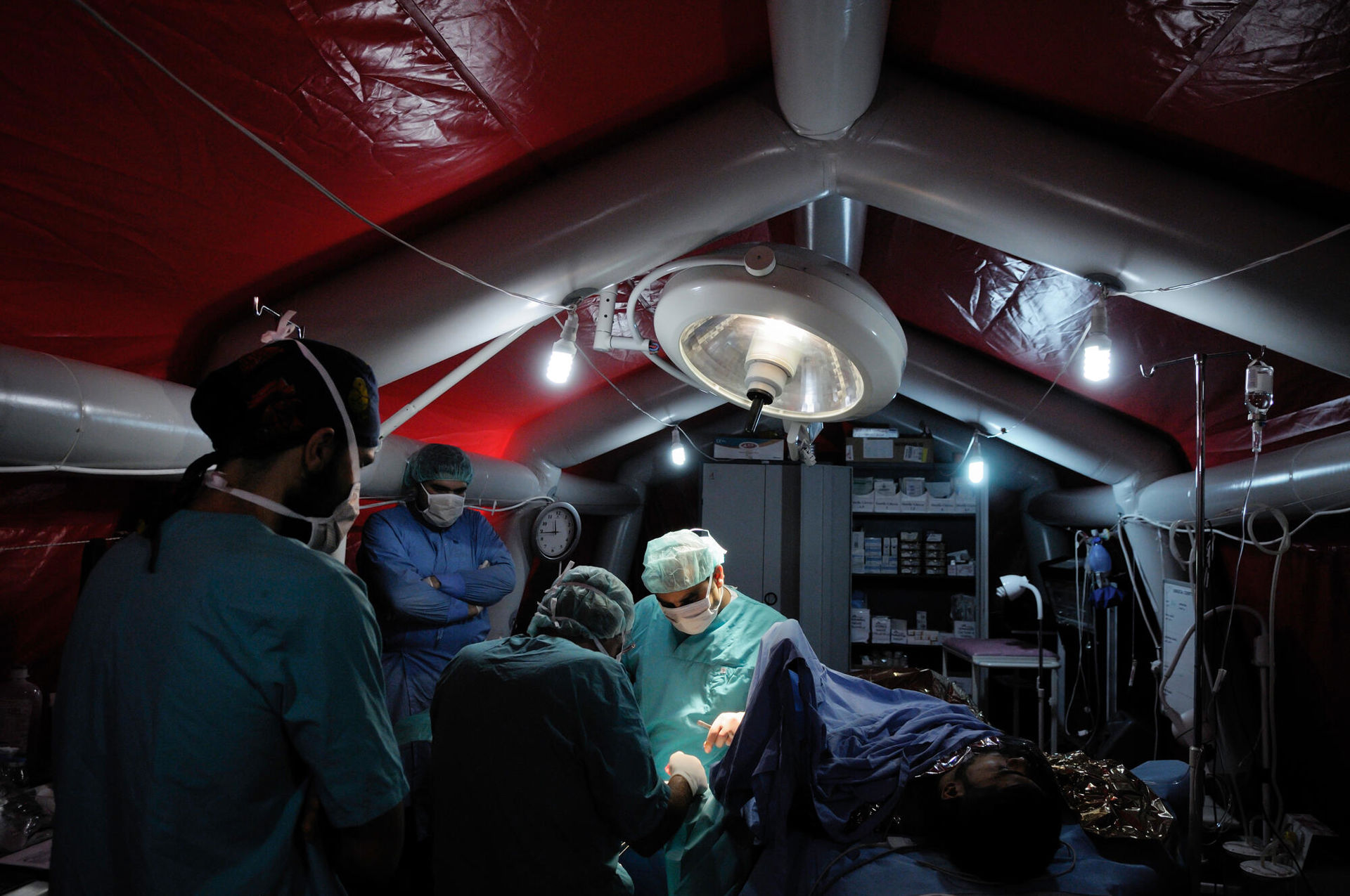 Field hospitals in unlikely places, December 2012.As frontlines shift in northwest Syria, MSF converts a disused chicken farm into a field hospital, providing emergency trauma surgery as well as primary and secondary medical care. ©Robin Meldrum/MSF
Field hospitals in unlikely places, December 2012.As frontlines shift in northwest Syria, MSF converts a disused chicken farm into a field hospital, providing emergency trauma surgery as well as primary and secondary medical care. ©Robin Meldrum/MSF
As numbers of Syrian refugees increased in neighbouring countries, MSF expanded its activities in places such as Lebanon’s Bekaa Valley and camps set up in Domeez, Iraqi Kurdistan. Increasing numbers of Syrian refugees were also seeking refuge further afield, moving away from the Middle East and towards Europe.
 Syrian refugees in Iraq, May 2012. MSF starts working in Domiz refugee camp, Iraq, becoming the main provider of healthcare for Syrian refugees sheltering there. ©Michael Goldfarb/MSF
Syrian refugees in Iraq, May 2012. MSF starts working in Domiz refugee camp, Iraq, becoming the main provider of healthcare for Syrian refugees sheltering there. ©Michael Goldfarb/MSF
2013: Syrians’ needs increase
By 2013, Syrians were not only exposed to high levels of violence, but also to the direct consequences of a dysfunctional and deteriorating health system. MSF teams started to witness the resurgence of preventable diseases. Cases of measles among children in Aleppo, and the discovery of the first case of polio in Syria in 14 years, were early indications of a health system breakdown in the country as a result of the war, which led to mass vaccination campaigns by MSF in northeast Syria.
Medical organisations in the country also started to voice more strongly their difficulties in meeting people’s needs, let alone dealing with mass casualties and acute emergencies. Due to the intensity of fighting in southern Syria, we opened an emergency surgical programme in Ramtha, northern Jordan, near the Syrian border, to treat war-wounded people unable to receive treatment in the 14 field hospitals in Dara’a.
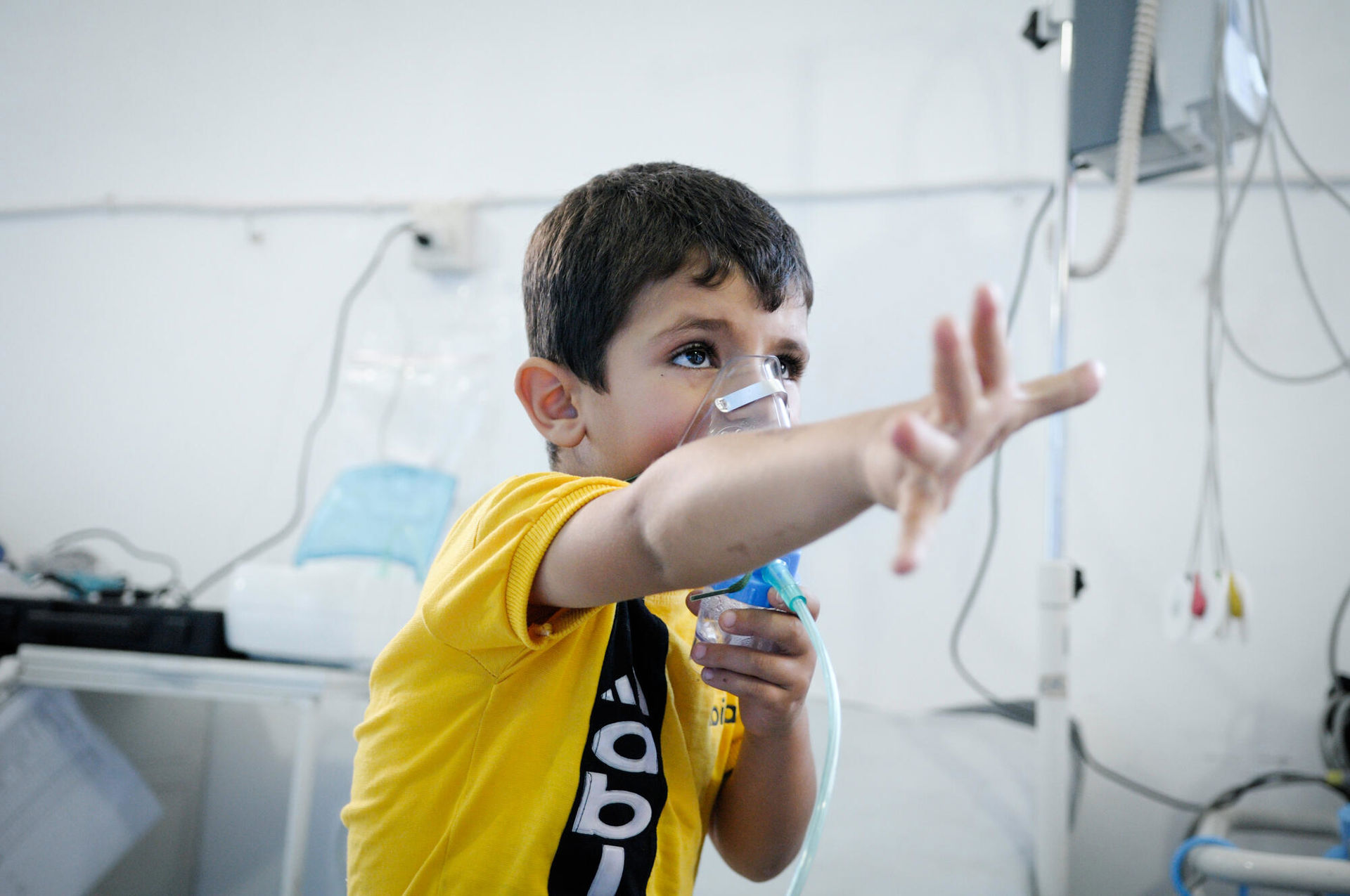 July 2013. A boy with asthma receiving oxygen in the ER section of an MSF hospital in Syria. The dust had aggravated his asthma and he arrived at the MSF hospital unable to breathe. It was impossible for his parents to find an asthma inhaler in Syria. ©Robin Meldrum/MSF
July 2013. A boy with asthma receiving oxygen in the ER section of an MSF hospital in Syria. The dust had aggravated his asthma and he arrived at the MSF hospital unable to breathe. It was impossible for his parents to find an asthma inhaler in Syria. ©Robin Meldrum/MSF
Meanwhile, hundreds of thousands of Syrians were still leaving Syria to seek safety or medical treatment in nearby countries. These nations, experiencing a continuous influx of refugees, started adopting more restrictive border policies. In response, we further expanded the volume of our operations in the region to provide as much assistance as possible to the Syrian people. By the end of 2013, an estimated 1.5 million Syrians were refugees.
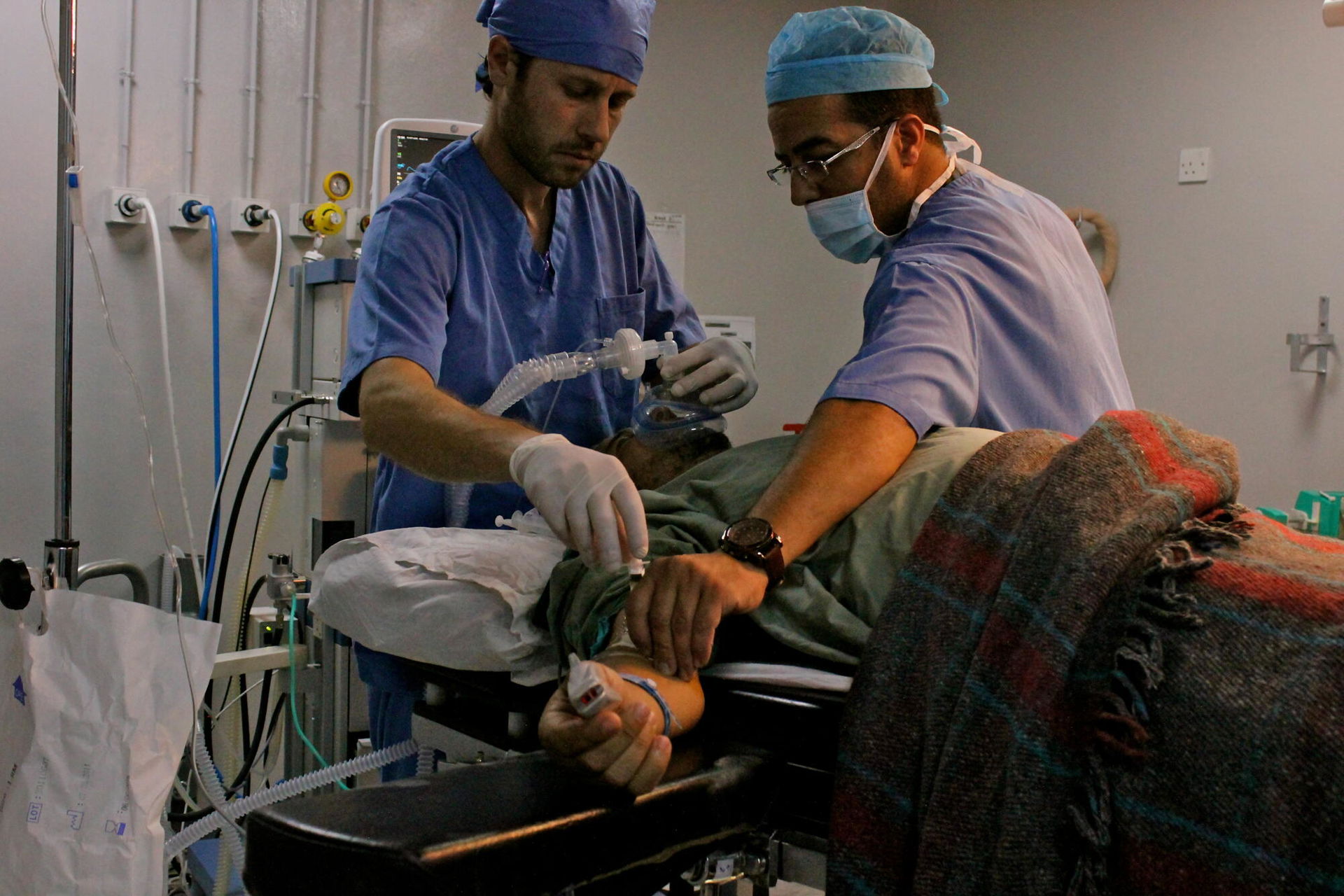 September 2013. Increased surgical activities in Jordan MSF opens an emergency surgical programme in the Jordanian town of Ramtha, close to the Syrian border, where we treat hundreds of war-wounded patients from southern Syria. ©Diala Ghassan/MSF
September 2013. Increased surgical activities in Jordan MSF opens an emergency surgical programme in the Jordanian town of Ramtha, close to the Syrian border, where we treat hundreds of war-wounded patients from southern Syria. ©Diala Ghassan/MSF
2014: Deadly clashes intensify
In 2014, the war grew increasingly bloody. The UN estimated that 6.5 million people had been internally displaced, while more than three million had fled Syria.
Violence and insecurity, the tightening of sieges and increased shelling, and attacks on health facilities and medical workers, were some of the challenges faced by MSF teams, which prevented them from providing a more extensive programme of medical humanitarian aid.
The abduction of MSF staff in 2014 also led us to stop our activities in areas controlled by the Islamic State (IS) group and to withdraw international staff in northwest Syria. Yet, we still managed to maintain our presence in Syria, opening new projects and increasing our remote support to medical facilities within the country.
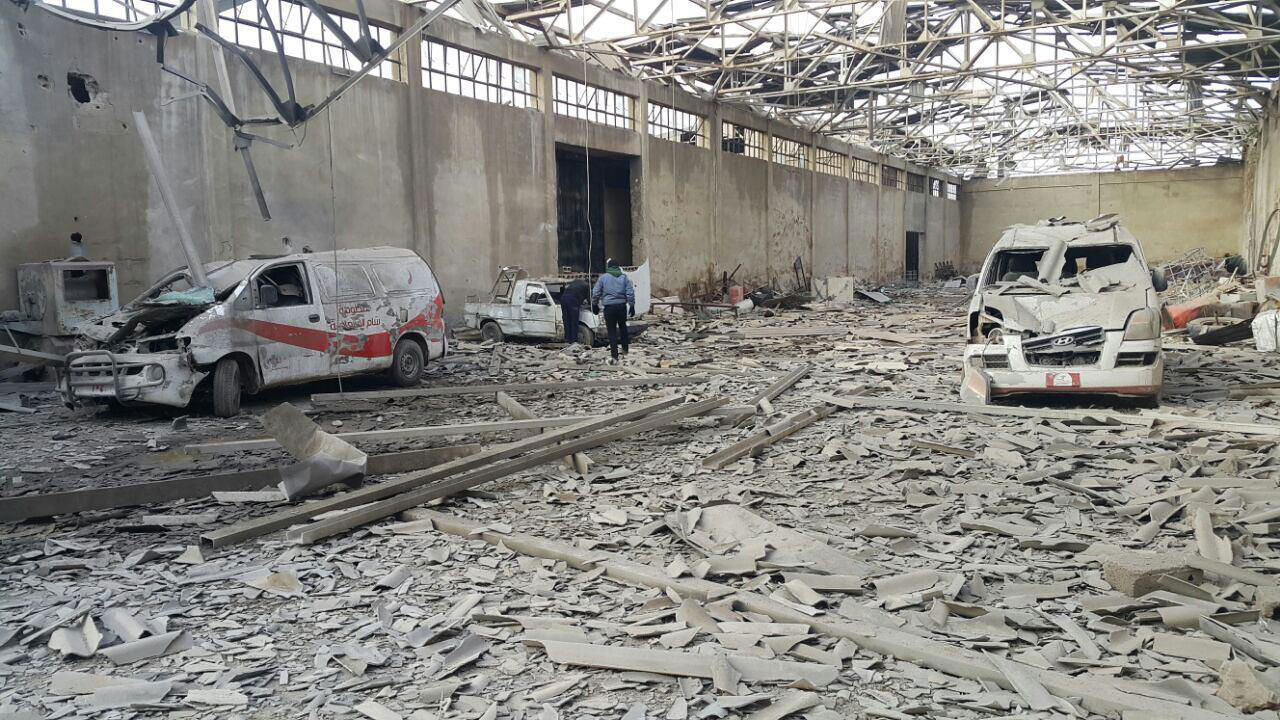 Nowhere to go, October 2014. Hundreds of casualties are reported in the town of Erbin in east Ghouta, a suburb of Damascus, following the bombing of a crowded market. Some 50,000 people have been under siege in east Ghouta for more than two years. This photo was taken in December 2016, the last two functional ambulances in Al-Marj neighbourhood (in the East Ghouta besieged area near Damascus) were destroyed beyond repair in an aerial bomb attack on 05 December 2016.©MSF
Nowhere to go, October 2014. Hundreds of casualties are reported in the town of Erbin in east Ghouta, a suburb of Damascus, following the bombing of a crowded market. Some 50,000 people have been under siege in east Ghouta for more than two years. This photo was taken in December 2016, the last two functional ambulances in Al-Marj neighbourhood (in the East Ghouta besieged area near Damascus) were destroyed beyond repair in an aerial bomb attack on 05 December 2016.©MSF
2015: Huge displacement crisis
In 2015, the number of Syrian refugees who had fled the country crossed the four million mark, with thousands attempting dangerous crossings of the Mediterranean Sea, while another six million people were internally displaced within Syria. The conflict had caused the biggest displacement crisis since the Second World War, leaving millions in desperate need of lifesaving humanitarian aid. We increased our activities across the region in response, launching search and rescue operations in the Mediterranean Sea, and supporting people along their journeys to Europe.
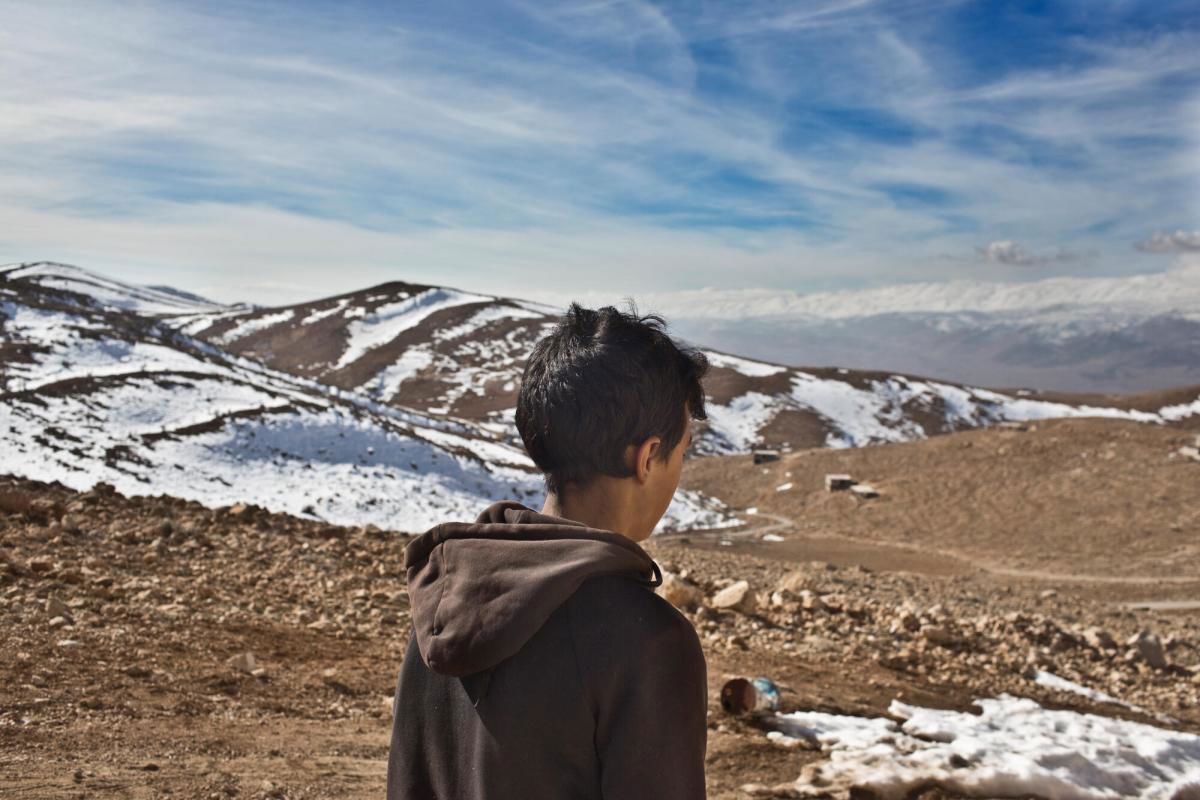
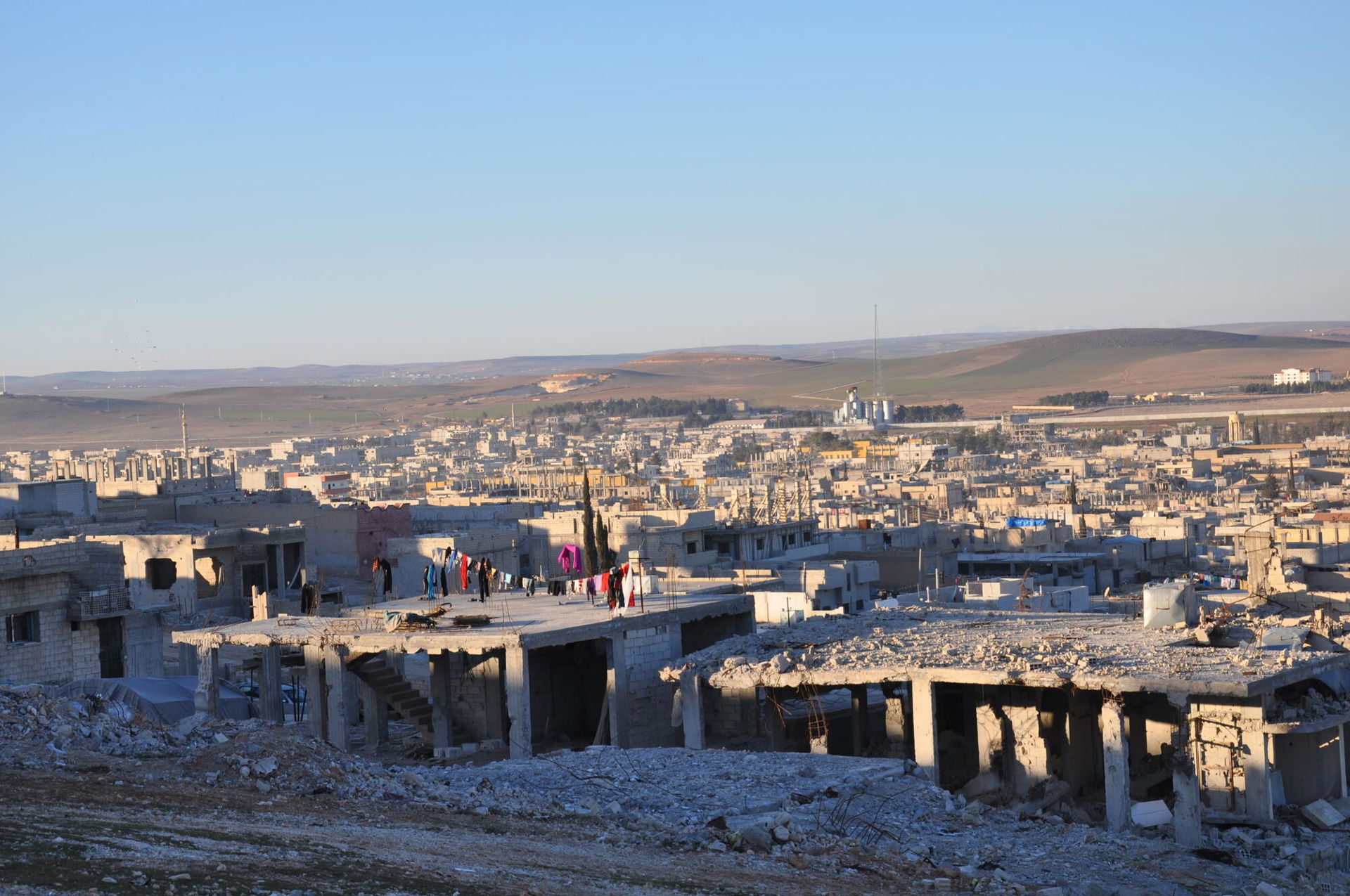 View of Kobane from the top of a nearby mountain, Kobane, Meshta Nour mountain, January 25, 2017. ©Jamal Bali
View of Kobane from the top of a nearby mountain, Kobane, Meshta Nour mountain, January 25, 2017. ©Jamal Bali
With more foreign countries and parties entering the war, 2015 was characterised by extreme violence, affecting the lives of millions of people. Civilian areas were routinely bombed, often in ‘double-tap’ attacks, in which the initial strike is followed by a second strike, targeting rescue teams or the health facility receiving the wounded. There were also numerous reports of attacks resulting in symptoms of exposure to chemical agents. At least 1.5 million people were trapped in besieged areas without access to humanitarian aid, healthcare or medical evacuation.
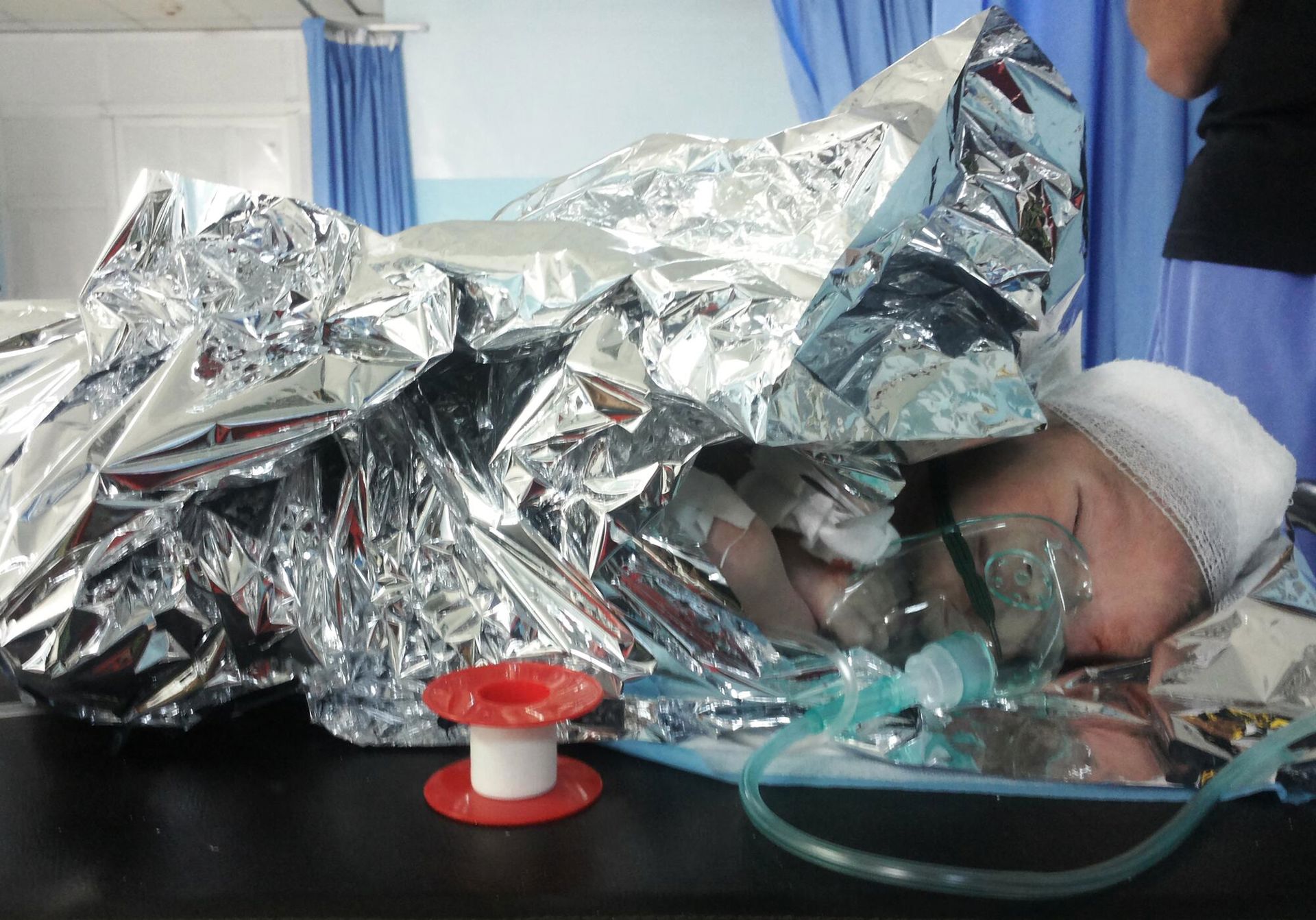 Majed, 27-day old new-born, arrived at MSF surgical project in Ramtha with a head injury due to an explosive barrel bomb. ©Renate Sinke/MSF
Majed, 27-day old new-born, arrived at MSF surgical project in Ramtha with a head injury due to an explosive barrel bomb. ©Renate Sinke/MSF
Within Syria, 2015 marked the year in which MSF supported the highest number of health facilities to date, reaching more than 150 health facilities. However, our support did not prevent these facilities from being directly impacted by the conflict. In 2015, 23 MSF-supported Syrian health staff were killed and 58 were wounded. Furthermore, 63 MSF-supported hospitals and clinics were bombed or shelled on 94 separate occasions in 2015, and 12 of these facilities were completely destroyed.
We gained access to the heavily destroyed city of Kobanê/Ain Al-Arab, after the IS group was forced out by Kurdish forces with the support of coalition forces. We built a hospital in the city, only for it to be destroyed following another intense period of conflict after Kobanê was infiltrated by fighters from the Islamic State group. Despite this, MSF continued to support primary and secondary healthcare in the city.
2016: A trapped population
In 2016, siege tactics continued, double-tap attacks increased, and intensified bombing and shelling led to the humanitarian crisis inside the country becoming even more dire. By then, many civilian areas had been routinely bombed and deprived of aid. Accessing food and health services were extremely difficult for many people, especially those living in places under siege.
In December, the Syrian government re-took east Aleppo, but not until its residents had lived through the fiercest bombardment of the five-year war. East Aleppo became the epitome of the Syrian conflict, with every atrocity committed in one place: siege warfare; the destruction of multiple hospitals; indiscriminate bombing of civilian areas; and a total disregard for the rules of war. MSF was fully or partially supporting eight hospitals in east Aleppo – all of them were hit by bombs.
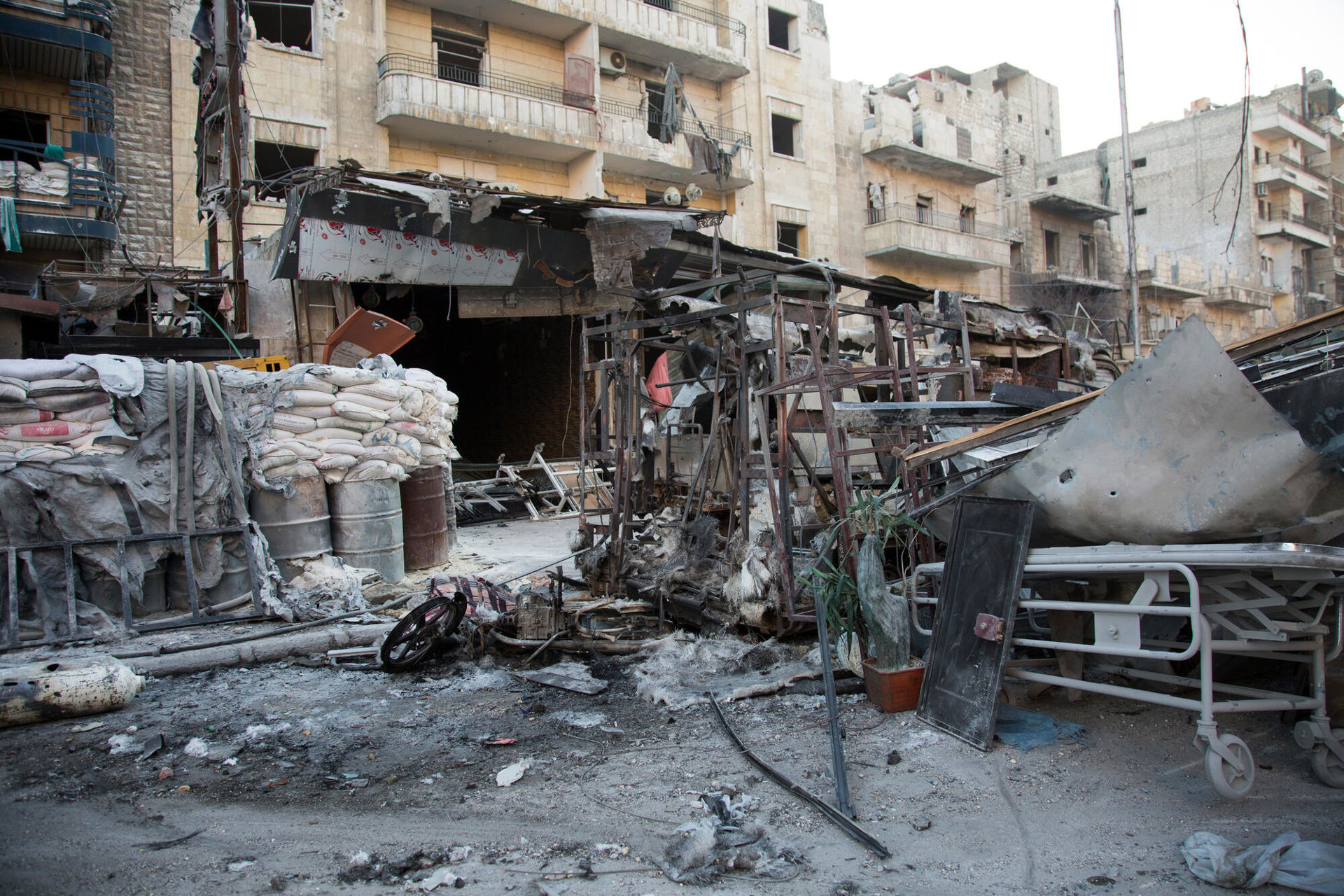 The airstrikes shattered everything on the surroundings, including ambulances and cars parked in the front of the hospital. ©Karam Almasri
The airstrikes shattered everything on the surroundings, including ambulances and cars parked in the front of the hospital. ©Karam Almasri
Medical facilities, staff and patients continued to be victims of indiscriminate and targeted attacks. In 2016, 32 medical facilities receiving our support were bombed or shelled on 71 separate occasions.
Meanwhile, more of Syria’s neighbouring countries had closed their borders to refugees, leaving many people trapped in areas under siege or stranded at the closed borders. This stranding of people occurred at the Jordanian border, blocking access to lifesaving activities for the war-wounded.
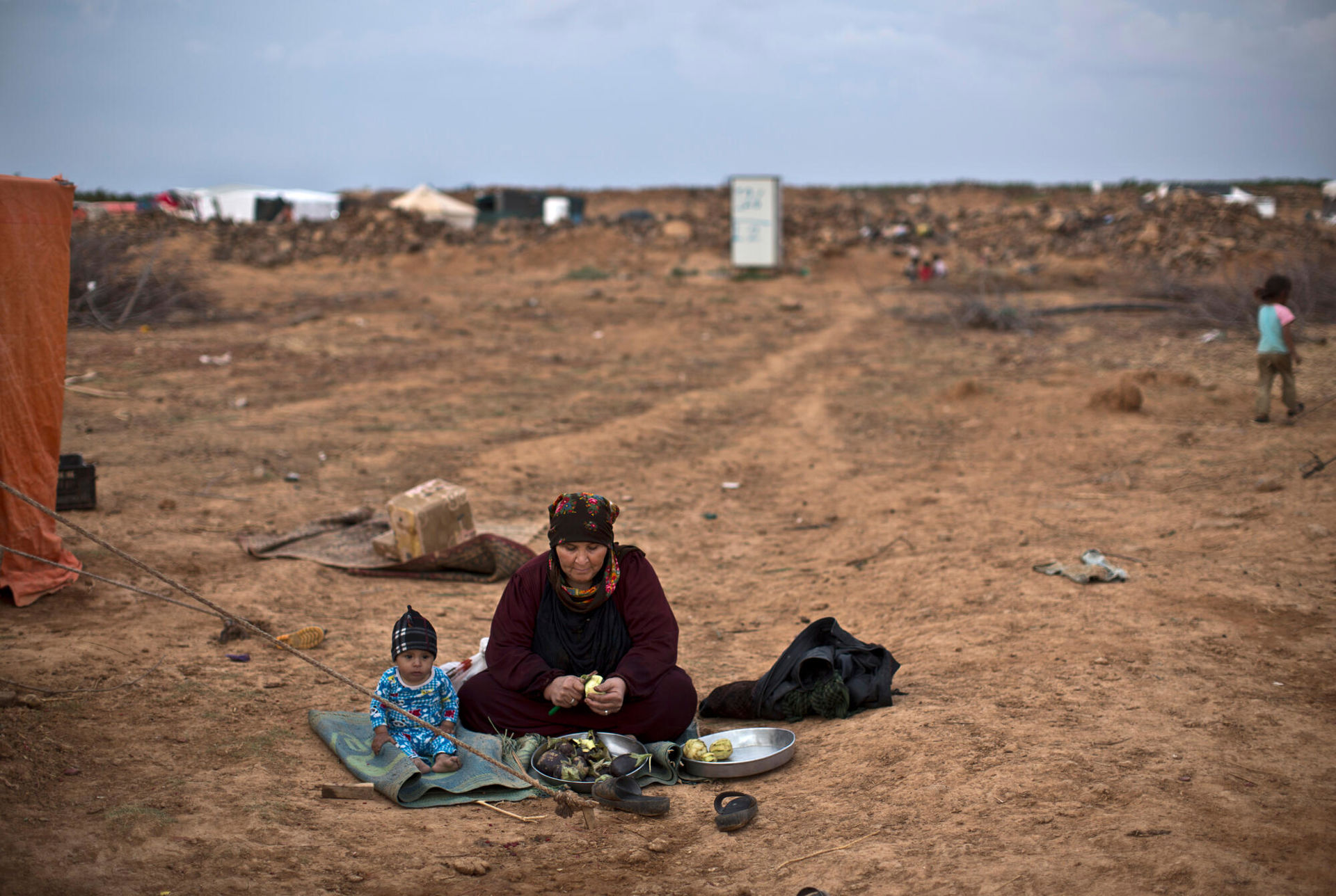 June 2016. Some 60,000 people are stuck in extremely harsh conditions close to Jordan’s northeast border, which was closed following a suicide attack that killed seven Jordanian soldiers. In the wake of the attack, MSF was forced to suspend its mobile clinic for Syrians gathered at the Berm – an isolated and inhospitable border area of desert between Jordan and Syria where thousands of Syrians fleeing the conflict were trapped. ©HH
June 2016. Some 60,000 people are stuck in extremely harsh conditions close to Jordan’s northeast border, which was closed following a suicide attack that killed seven Jordanian soldiers. In the wake of the attack, MSF was forced to suspend its mobile clinic for Syrians gathered at the Berm – an isolated and inhospitable border area of desert between Jordan and Syria where thousands of Syrians fleeing the conflict were trapped. ©HH
2017: A race for territory
A race to secure territory and control emerged as the main geopolitical change of the year. After a major military offensive on Raqqa, the IS group lost control over large areas of territory in the northeast to US-backed Syrian Democratic Forces. MSF treated hundreds of war-wounded people as a result of the intense bombing offensive in Raqqa, as well as those severely injured by booby traps and unexploded ordinances left behind in people’s destroyed homes.
Meanwhile, in the south of the country, the Syrian government began retaking territories in the provinces of Dara’a, Quneitra and Suwayda. These events had major consequences on the lives of hundreds of thousands of people living in these areas due to the heavy shelling.
These changes in dynamics and the balance of power disrupted our activities in some of the areas where we worked. A total of 11 medical facilities that we supported were hit by bombs or shells on 12 occasions in targeted or indiscriminate attacks.
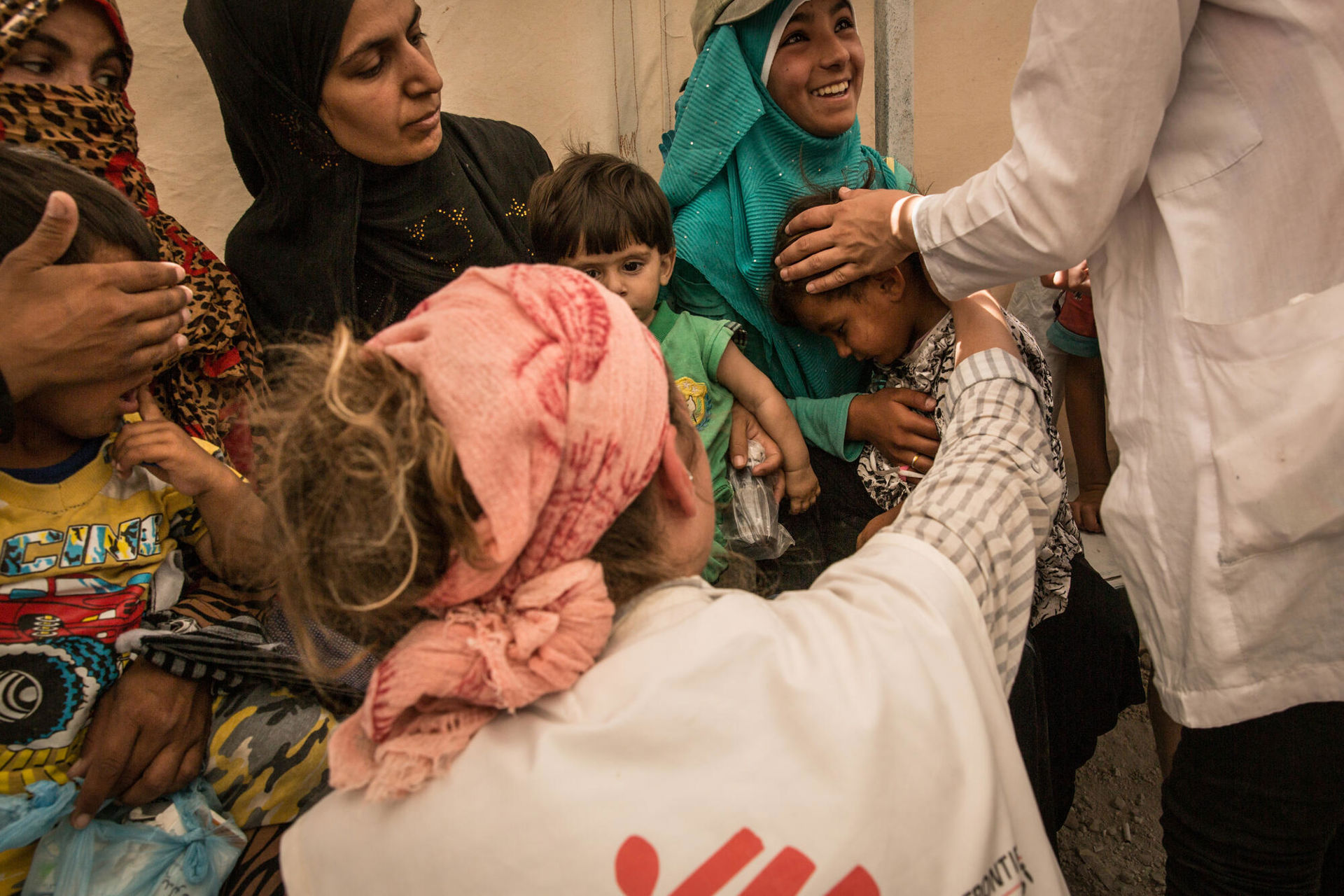 July 2017. MSF Clinic in Aïn Issa Displaced Camp, Kurdish province,Syria. Emilie, a French doctor, inspects a baby who has a fever before proceeding with a medical consultation. His mother is displaced from Raqqa. ©Chris Huby
July 2017. MSF Clinic in Aïn Issa Displaced Camp, Kurdish province,Syria. Emilie, a French doctor, inspects a baby who has a fever before proceeding with a medical consultation. His mother is displaced from Raqqa. ©Chris Huby
2018: Waves of displacement and return
With intense fighting to gain control over disputed regions, and with the military advances of Syrian government forces, new waves of displacement began arriving in northwest Syria. These followed surrender terms imposed by the government granting safe passage for fighters and civilians who wanted to be transported to other non-government-controlled areas of the country, most often to Idlib province. Meanwhile in the northeast, people were coming back to ruined towns and cities full of booby traps and landmines.
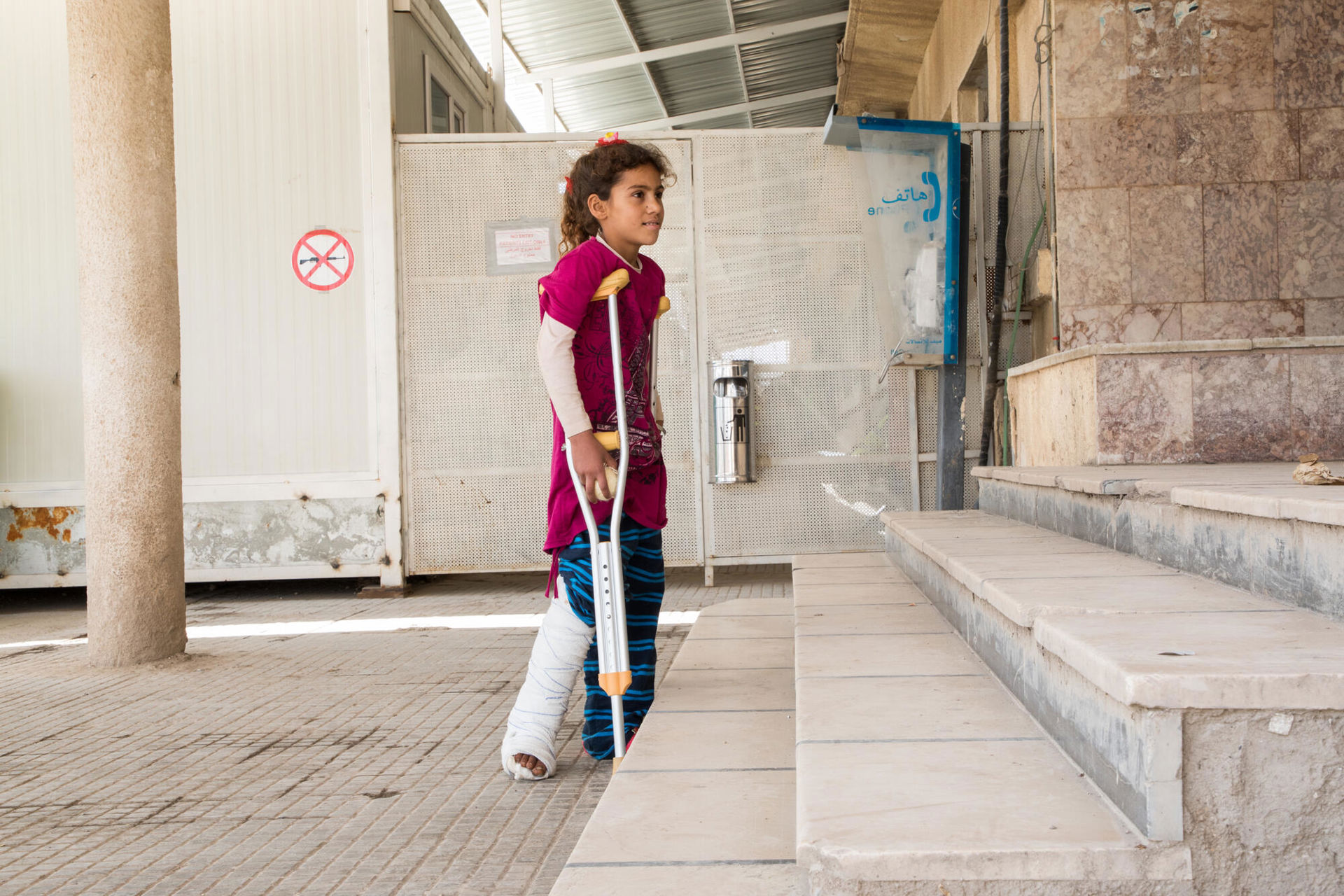 April 2018. As relative calm returns to Hassakeh and Raqqa provinces, people previously displaced by heavy fighting begin returning home, to areas littered with landmines and unexploded remnants of war, and where the health infrastructure has been largely destroyed. MSF teams in Hassakeh and Raqqa treat hundreds of patients wounded by landmines, booby traps and explosive ordnance. ©Louise Annaud/MSF
April 2018. As relative calm returns to Hassakeh and Raqqa provinces, people previously displaced by heavy fighting begin returning home, to areas littered with landmines and unexploded remnants of war, and where the health infrastructure has been largely destroyed. MSF teams in Hassakeh and Raqqa treat hundreds of patients wounded by landmines, booby traps and explosive ordnance. ©Louise Annaud/MSF
Between February and April, east Ghouta, in the suburbs of Damascus, witnessed one of the heaviest bombardments since the beginning of the war. Many health facilities were hit and around 2,000 people were killed during the offensive, which ended with the Syrian government taking control of the suburb.
In many places, such as Dara’, east Ghouta, Hama and Homs, MSF was unable to continue its work and support to medical facilities after these areas were retaken by the Syrian government. At this time we increased our medical support in the north of the country.
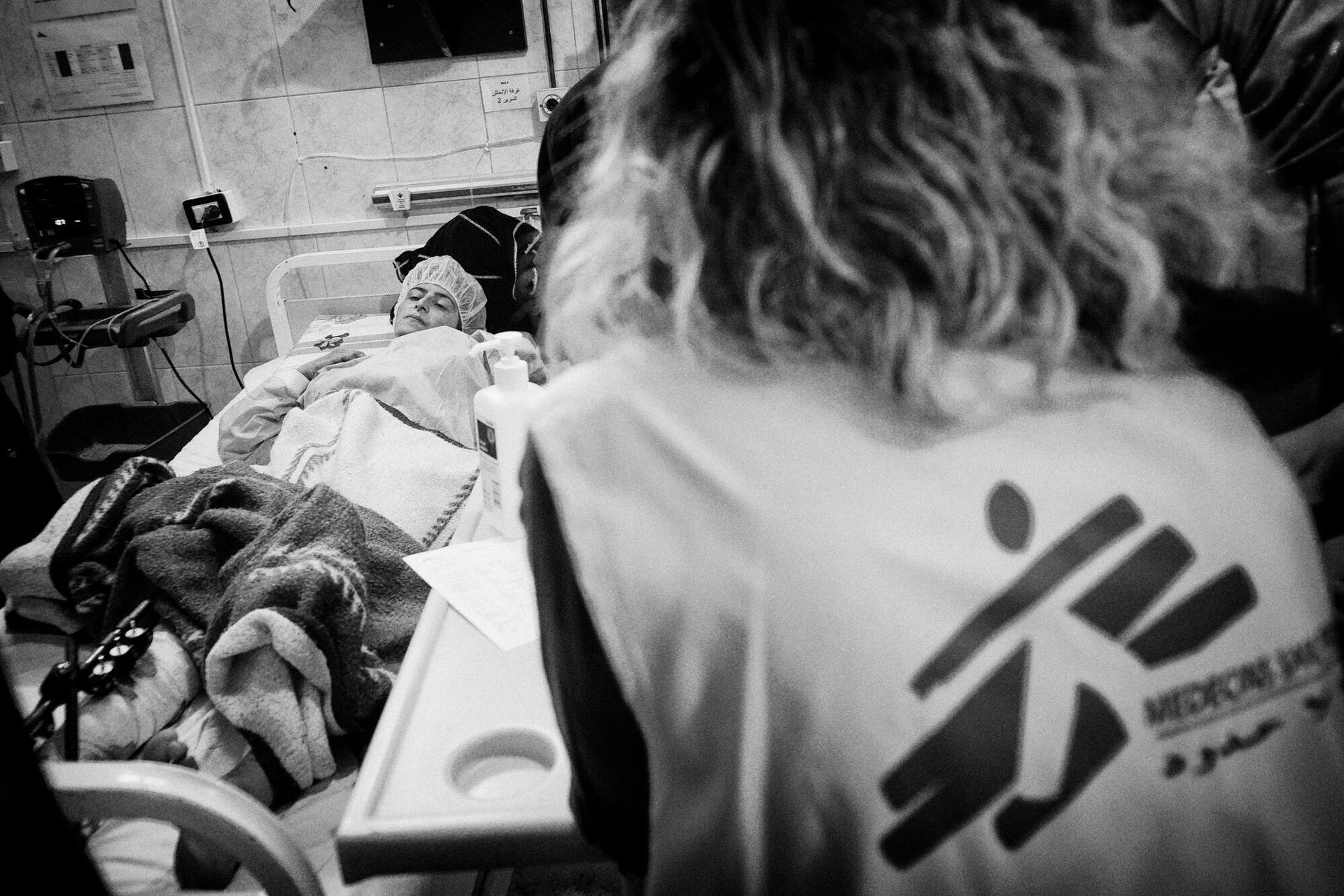 May 2018. MSF started rehabilitating parts of Raqqa national hospital, continued to support the paediatric, maternity and surgical wards of Tal Abyad hospital to the north, and supported or administered vaccination campaigns across the Raqqa governorate. ©Eddy Van Wessel
May 2018. MSF started rehabilitating parts of Raqqa national hospital, continued to support the paediatric, maternity and surgical wards of Tal Abyad hospital to the north, and supported or administered vaccination campaigns across the Raqqa governorate. ©Eddy Van Wessel
2019: Military operations in the north
In 2019, the conflict continued, mainly affecting the north of Syria.
In northwest Syria, hundreds of thousands of people were displaced as a consequence of an offensive launched by Syrian government forces and their allies, notably Russia, in Idlib province, the country’s last opposition stronghold. Most newly displaced people headed for areas where no clean water or medical care was available. They had few options, as most areas that were considered relatively safe were already overcrowded and overstretched in terms of humanitarian assistance.
 October 2019.Following the launch of Turkish military operations in northern Syria, residents flee towns and villages along the border to escape the heavy shelling. MSF teams try to meet their growing needs for medical care and humanitarian assistance. ©Delil Souleiman/AFP
October 2019.Following the launch of Turkish military operations in northern Syria, residents flee towns and villages along the border to escape the heavy shelling. MSF teams try to meet their growing needs for medical care and humanitarian assistance. ©Delil Souleiman/AFP
In northeast Syria, MSF scaled up activities as a rapid influx of more than 60,000 displaced people arrived at Al-Hol camp, most of them from the IS group’s last strongholds of Deir Ez-Zor Governorate. Later that year, the Turkish military, alongside allied Syrian armed opposition groups, launched the ‘Peace Spring’ operation, aimed at clearing the Kurdish People’s Protection Units from a strip of land 30 km long and 440 km wide along the Turkish border.
On top of continuous conflict and displacement, by 2019, Syria was going through its worst economic crisis in years and the Syrian pound reached an all-time low on the black market, making people’s lives even more difficult.
 October 2019.As people continue to flee the conflict in northeast Syria, MSF launches medical activities at a site receiving refugees in Iraq close to the border with Syria. ©MSF/Hassan Kamal Al-Deen
October 2019.As people continue to flee the conflict in northeast Syria, MSF launches medical activities at a site receiving refugees in Iraq close to the border with Syria. ©MSF/Hassan Kamal Al-Deen
2020: Military offensive, economic crisis and global pandemic
2020 started with the continuation of a huge military offensive in northwest Syria, resulting in the displacement of around one million people. Many of them were already displaced within the area and had fled the conflict multiple times in previous months or years.
The COVID-19 pandemic further worsened the already precarious health situation in Syria. Four months after the pandemic was officially declared, the disease made its way into Idlib, with a first case confirmed on 9 July. The first COVID-19 cases were among the medical community and this became a growing concern over the following months. Even prior to the outbreak, human resources were very limited in the health sector, hospitals in the region often having to share medical staff in order to remain open. In that sense, even just a few doctors infected by the virus and temporarily being put out of work could make a huge difference with regard to access to healthcare.
Meanwhile the economic crisis continued and the record-breaking depreciation of the Syrian pound became a reality for people in Syria, translating into an inability to access basic necessities such as housing, food and healthcare. Refugees in some neighbouring countries were also touched by economic crises in the host countries, as in Lebanon.
After nine years of war, the Syrian healthcare system was broken, with limited supplies, few medical staff and health facilities that were often closed or no longer functioning.
 September 2020.Northwest Syria sees a sharp increase in the number of patients with COVID-19, making an already dire situation even more challenging. ©Muhammed Said/Anadolu Agency via Getty Images
September 2020.Northwest Syria sees a sharp increase in the number of patients with COVID-19, making an already dire situation even more challenging. ©Muhammed Said/Anadolu Agency via Getty Images
March 2021
A decade later, the conflict in Syria is not over and the population continues to suffer. Its effects continue to have a disastrous impact on Syrians across the world. Currently, almost 12 million Syrians - half the pre-war population - are displaced inside and outside Syria. Some 5.6 million refugees are scattered throughout the world, the majority in Turkey, Lebanon, Jordan, Iraq and Egypt. 6.2 million people are internally displaced – the largest number worldwide – most of them living in precarious conditions.
A record 12.4 million Syrians - nearly 60 percent of the population - are now food insecure, according to alarming new national data from the UN World Food Programme (WFP). In just over one year, an additional 4.5 million Syrians have become food insecure. An economic crisis, job losses as a result of COVID19 and soaring food prices have added to the plight of Syrians who have been displaced and worn down by a decade of conflict.
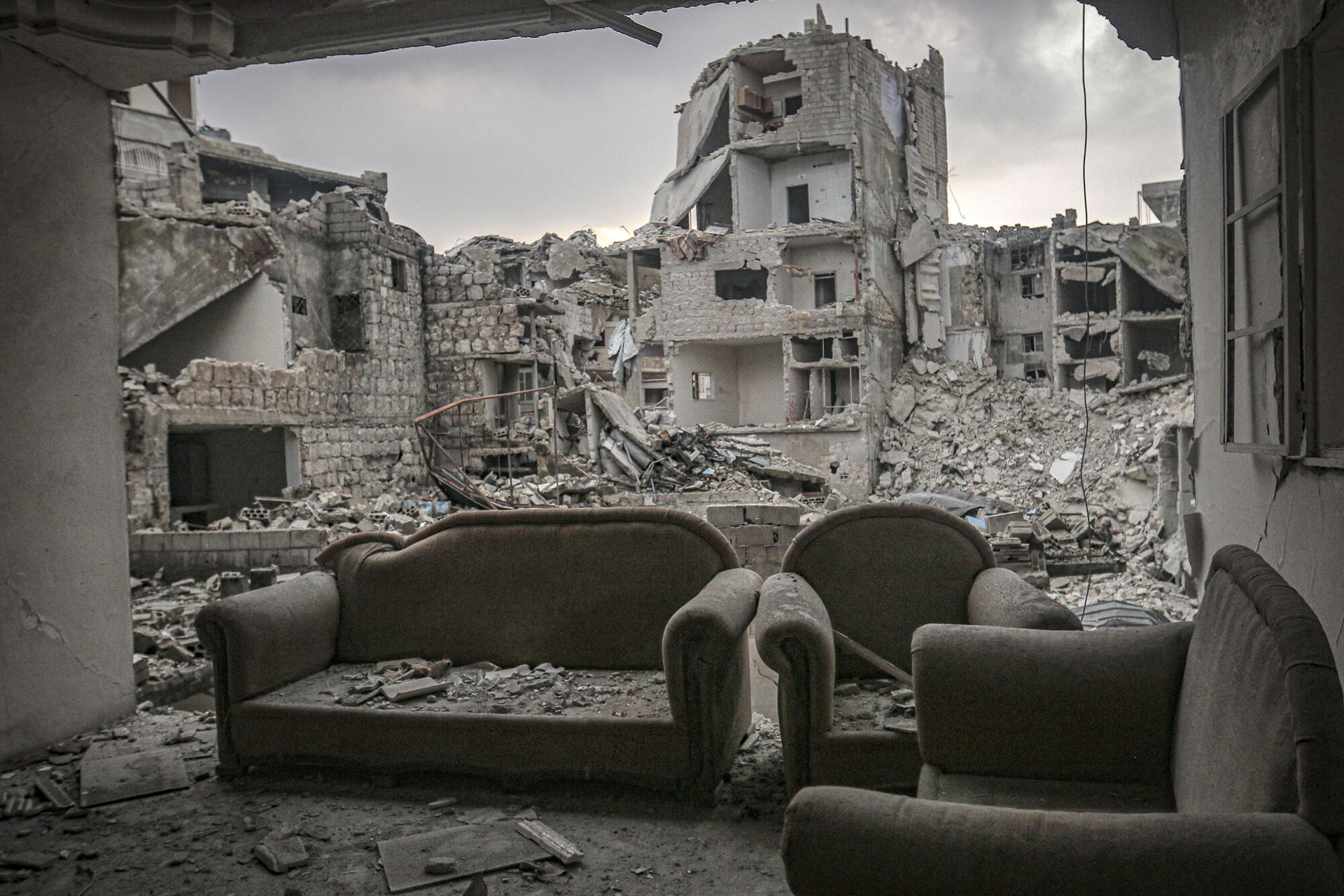 February 2020.MSF-supported hospitals near the frontlines in Idlib province receive 185 wounded and 18 patients who are dead on arrival as a result of indiscriminate attacks by the Syrian government and its allies on civilian areas. ©MSF/Hassan Kamal Al-Deen
February 2020.MSF-supported hospitals near the frontlines in Idlib province receive 185 wounded and 18 patients who are dead on arrival as a result of indiscriminate attacks by the Syrian government and its allies on civilian areas. ©MSF/Hassan Kamal Al-Deen